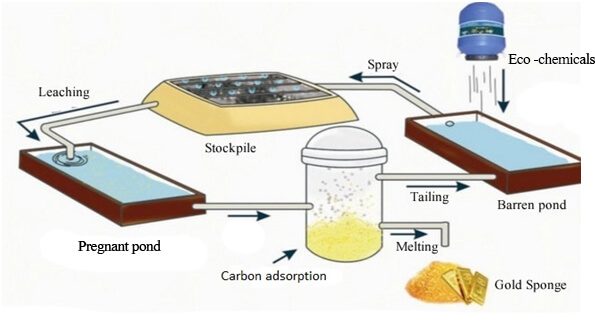
Acid leaching refers to a mineral leaching process in which an aqueous solution of inorganic acid is used as a leaching agent. It is one of the most commonly used leaching methods in chemical beneficiation. Sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, sulfurous acid, pyrosulfuric acid, hydrofluoric acid, aqua regia, etc. are all commonly used leaching agents.
Acid leaching is commonly performed by agitating an ore-leach mixture for 4 to as long as 48 hours at ambient temperature. Except in special circumstances, sulfuric acid is the leachant used; it is supplied in amounts sufficient to obtain a final leach liquor at about pH 1.5.