Learn about these 7 differences in jaw rock crusher!
As a widely used coarse-breaking equipment, the jaw rock crusher has been around for more than a century. Jaw fractures on the market today differ in their structure, shape, design, and materials. It is mainly introduced from seven perspectives in this paper: crushing cavity, frame, discharge port adjustment, motor installation, and bearing. By analyzing your needs, you can buy satisfactory products.
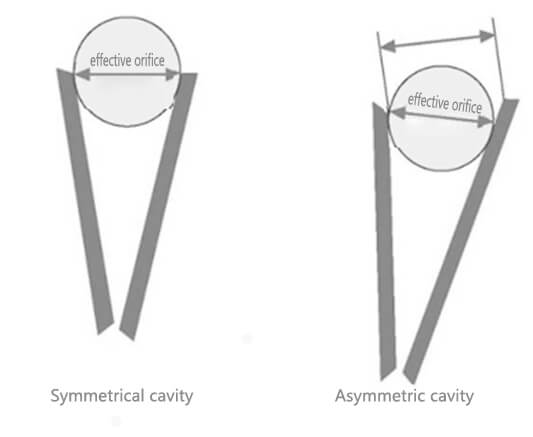
1. Crushing chamber
The crushing chamber is pivotal in determining the crusher’s efficiency. Traditional chambers feature straight-edged fixed jaws and beveled moving jaws, while newer designs employ symmetrical isosceles triangles. This innovation allows for a 5% larger feed particle size compared to traditional models, enhancing efficiency. The relationship between inlet size (D) and maximum feed particle size (f) is crucial: traditional crushers have f = 0.85d, whereas “Symmetrical isosceles triangle” crushers boast f = 0.9d. Additionally, the “mesh angle” between the jaws significantly impacts crushing force; a smaller angle results in greater force and higher efficiency. Advanced crushers have an included angle of 18°–21°, while traditional PE crushers range from 21°–24°.
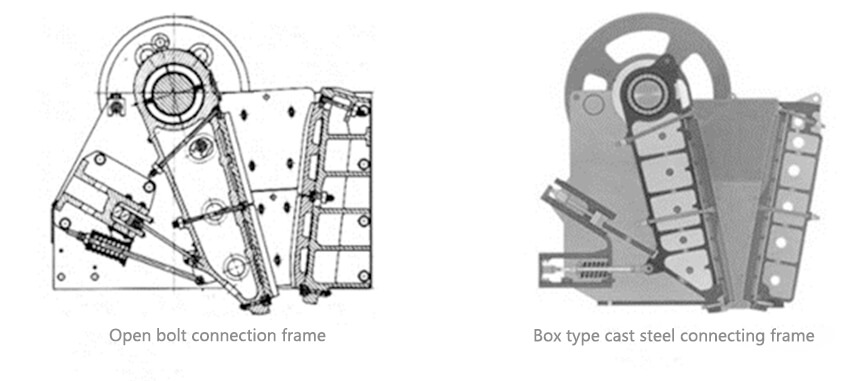
2. Rack
Jaw rock crusher frames come in various forms, including welded, bolted, open, and box frames, each offering distinct advantages in terms of durability and maintenance.
3. Ore outlet adjustment mechanism
Adjustment mechanisms are crucial for controlling output size. The two most common types are “gasket” and “wedge block” adjustments. Gasket adjustments are convenient and reliable, while wedge blocks offer ease of operation but slightly less reliability. Modern crushers increasingly use hydraulic cylinders for both the elbow plate and ore discharge port adjustments, particularly beneficial for mobile crushing stations.
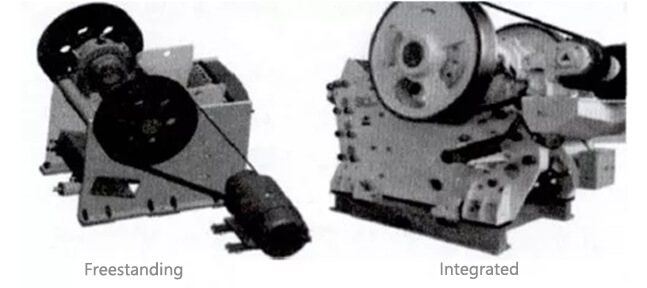
4. Motor installation type
Motors can be mounted on the crusher frame (integrated type) or on the foundation (independent type). Integrated types run on a triangular belt and are typically connected to the foundation via rubber gaskets, offering flexibility. Independent types require a bolted connection to the foundation, providing stability.
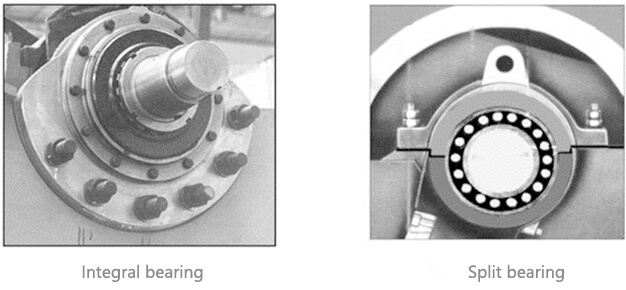
5. Type of bearing and bearing pedestal
Bearings are critical components, demanding high reliability and value. Their design and manufacturing must be precise to minimize maintenance costs and downtime. Therefore, the selection of bearings and bearing pedestals is paramount for crusher performance.
6. Startup and control
Start-up methods vary, including direct start, electronic soft starters, and variable resistance. Direct start is suitable for smaller motors, while variable resistance is ideal for winding motors due to their high blocking torque, making it a common choice for crushers.
7. Speed and stroke of crusher
The crusher’s speed and stroke are interdependent, affecting crushing efficiency. Speed is determined by the number of crushing cycles and discharge rate, with an optimal balance needed to prevent material from being ejected before adequate crushing. Stroke size influences crushing force; larger strokes result in greater force and better crushing. The crusher’s speed must adapt to the varying heights within the crushing chamber to ensure optimal performance.
In conclusion, understanding these critical aspects of jaw rock crushers empowers mine owners to select equipment that maximizes efficiency and productivity. By comparing different models and understanding their relative advantages, you can make a well-informed decision that aligns with your operational needs.
We can provide you with more information about beneficiation. If you have any questions, please contact: Whatsapp:+86 133 1927 7356
Email:[email protected]