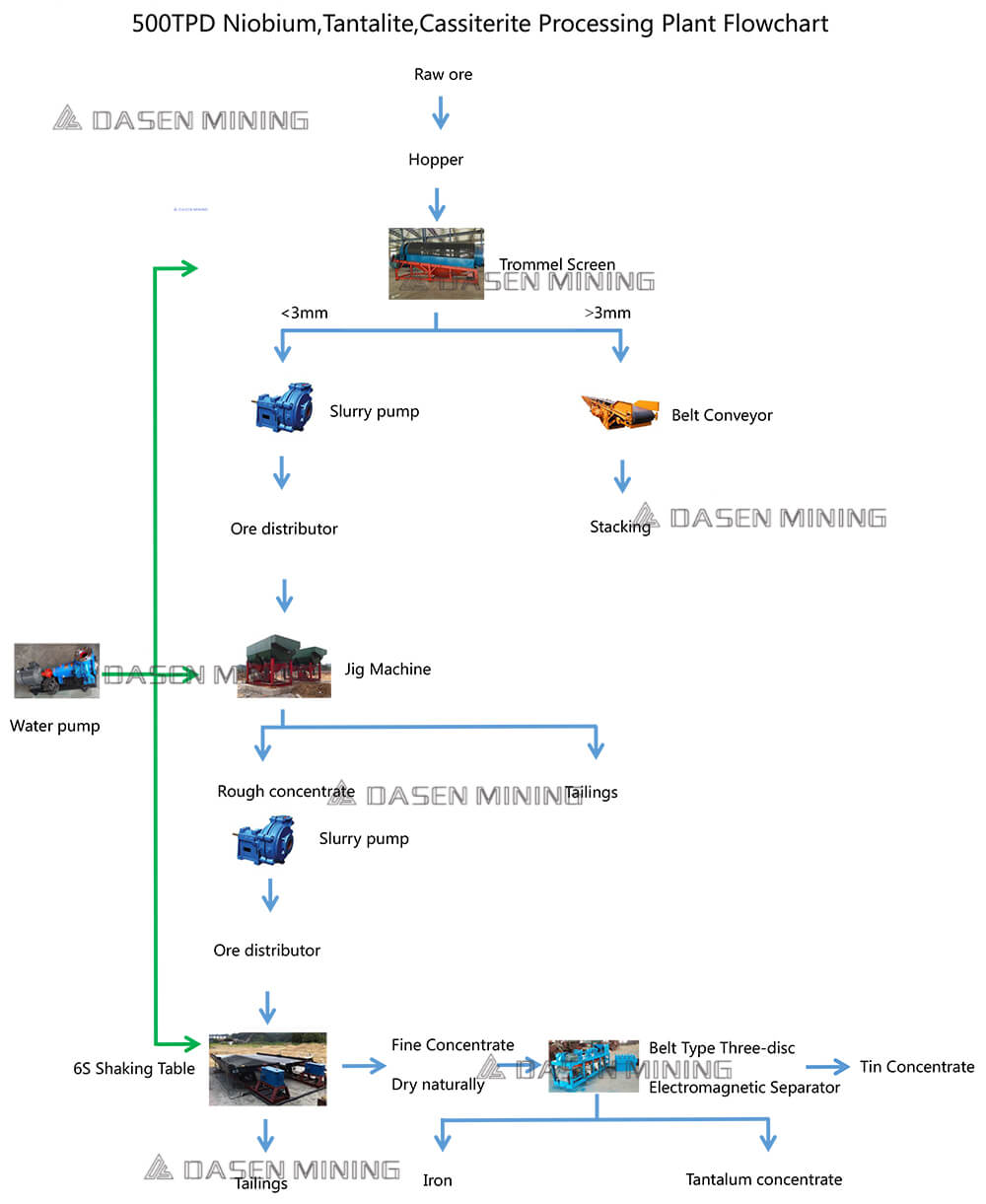
How to Efficiently Separate Tin and Tantalum-Niobium Ores Using a Three-Disc Magnetic Separator
The co-existence of tin and tantalum-niobium ores in mineral deposits often challenges effective separation. However, advancements in mineral processing technology, particularly magnetic separation, have made it possible to isolate these valuable minerals efficiently. This article explores the process of separating tin and tantalum-niobium ores, focusing on utilizing three-disc magnetic separators.
Understanding the Separation Process
The fundamental principle behind separating tin and tantalum-niobium ores lies in their distinct physical properties. Tantalum-niobium minerals generally exhibit a lower magnetic susceptibility compared to tin ores, which may contain magnetic impurities like magnetite.
Comminution: The ore is crushed and ground to a suitable particle size, typically less than 2mm.
Screening: The crushed ore is screened to remove oversized particles.
Magnetic Separation: The screened ore is fed into the three-disc magnetic separator. Magnetic particles are attracted to the magnetic discs, while non-magnetic particles pass through.
Drying: The separated fractions may be dried to improve the efficiency of subsequent processes.
Additional Separation Techniques
While magnetic separation is a primary method, other techniques may be employed in conjunction to enhance the overall separation efficiency, such as:
Gravity Separation: This method utilizes the density differences between minerals.
Froth Flotation: This technique exploits the surface properties of minerals to selectively attach to air bubbles, forming a froth.
Three-disc magnetic separators have proven to be effective tools for separating tin and tantalum-niobium ores. By understanding the principles of magnetic separation and the advantages offered by these separators, mineral processing engineers can optimize their operations and achieve higher product purity.
Whatsapp:+86 133 1927 7356
Email:[email protected]