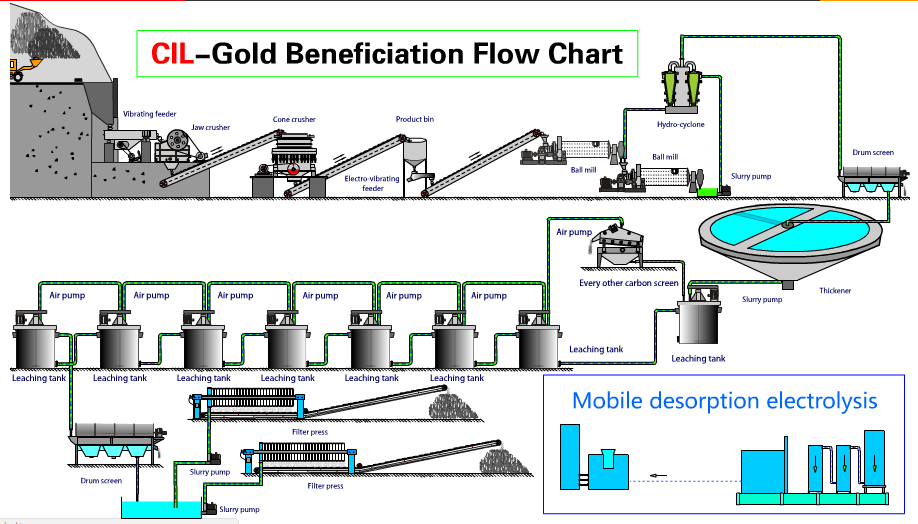
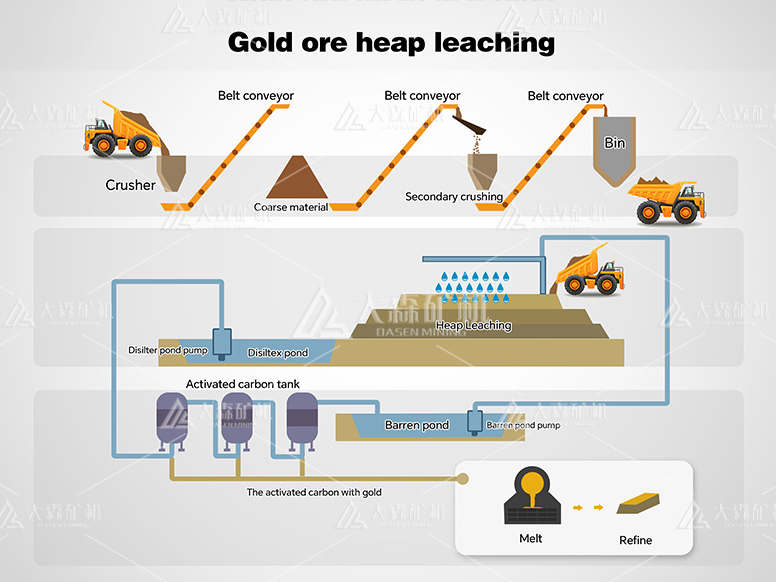
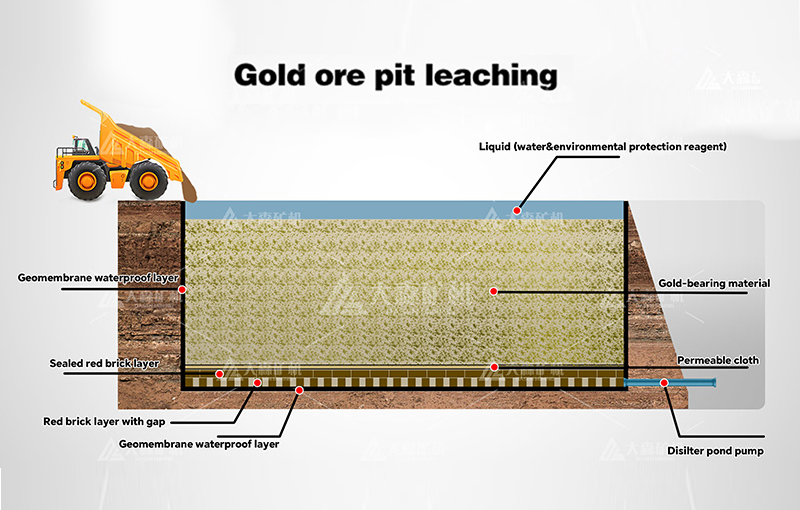
The gold cyanidation process, also known as gold CIL (Carbon in Leach) or CIP (Carbon in Pulp), is a hydrometallurgical technique used to extract gold from ore by converting the gold into a water-soluble coordination complex. This method is the most widely used leaching process for gold extraction, accounting for approximately 90% of global gold production.
DASEN MINING boasts 30 years of experience in producing gold CIL/CIP equipment and managing EPC (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction) projects. We have completed over 60 projects worldwide.
The 10TPD mobile-type gold CIL plant is designed to process approximately 10 tons of raw gold ore daily, achieving a gold recovery rate of over 95%. The entire system is housed in three 40-foot HQ containers. Upon arrival at the customer’s mine site, it can be quickly connected to power and water, making it ready for immediate use. This mobile-type CIP plant is ideal for new investors, providing an excellent opportunity for industrial experimentation during the government licensing process.
DASEN MINING is a global leader in mineral beneficiation solutions, specializing in the processing of gold, copper, zinc-lead, tin, columbite, and more.
With 30 years of expertise, we are a leading global provider of mineral separation solutions.
Global Technical Service Team: Expert, Efficient, and Responsible.
China’s Premier Mineral Processing Laboratory
Gold Cyanidation Leaching Processing Flowsheet
The entire process includes five key steps: crushing, grinding, leaching, gold desorption electrolysis, and smelting. This comprehensive approach ultimately yields gold ingots with a purity of over 99.9%.